How is equilibrium price determined?
Updated 3/22/2024 Jacob Reed
Below is a review of how markets reach equilibrium. If you would like to get some practice with these concepts, head over to the Shifting Markets Review Game.
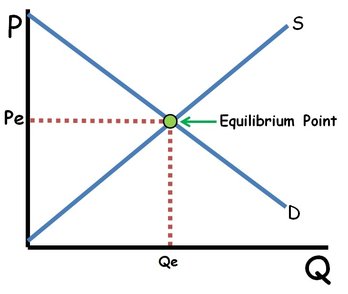
What is equilibrium?
Equilibrium is the price that clears the market. In other words it is the price where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. Market forces push prices toward equilibrium.
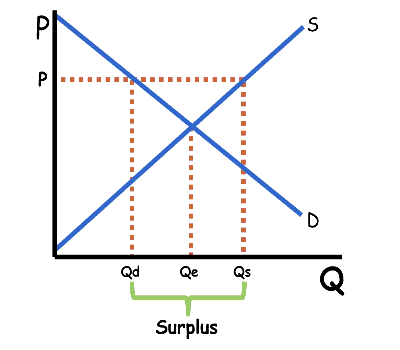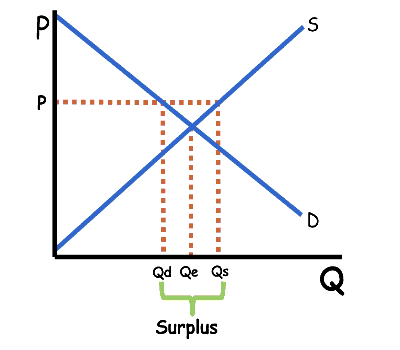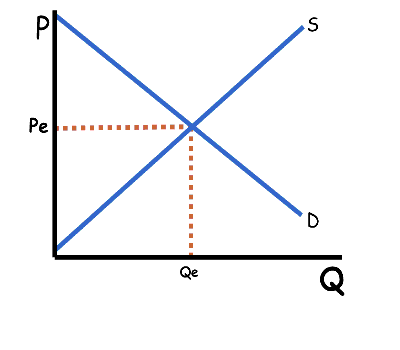
How does the market move toward equilibrium?
If the market price is above equilibrium, quantity supplied will be greater than quantity demanded, creating a surplus. When that occurs, suppliers have produced more than they are able to sell at the current price. The surplus induces suppliers to lower their price, (increasing Qd and decreasing Qs) until equilibrium is reached and the surplus is eliminated.
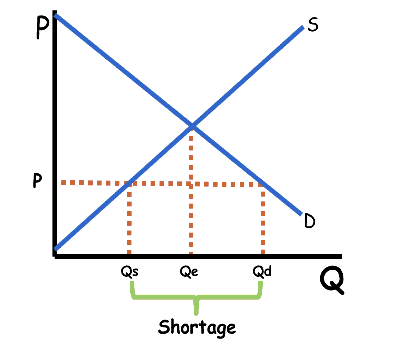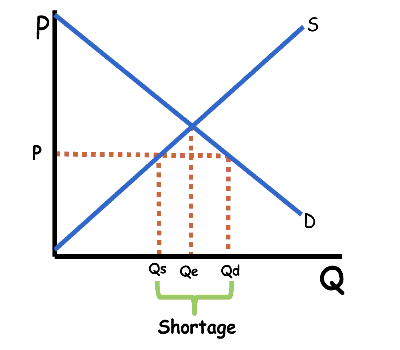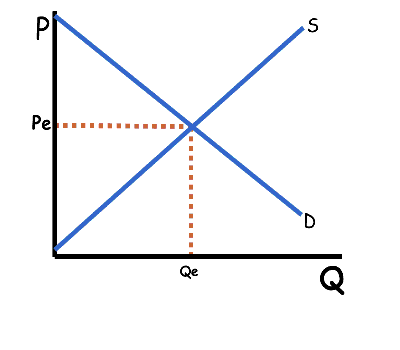
If the market price is below equilibrium, quantity supplied will be less than quantity demanded, creating a shortage. When that occurs, suppliers will sell out of the product and some customers will be left wanting. This induces sellers to raise their price toward equilibrium (decreasing Qd and increasing Qs) until equilibrium is reached and the shortage is eliminated.
How do shifts in supply and demand change equilibrium?
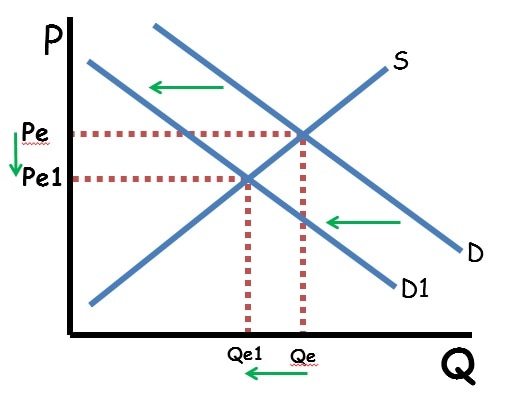
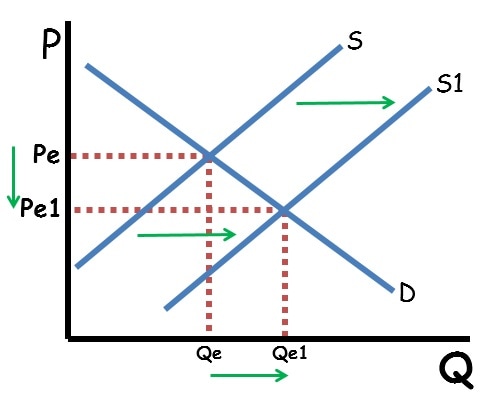
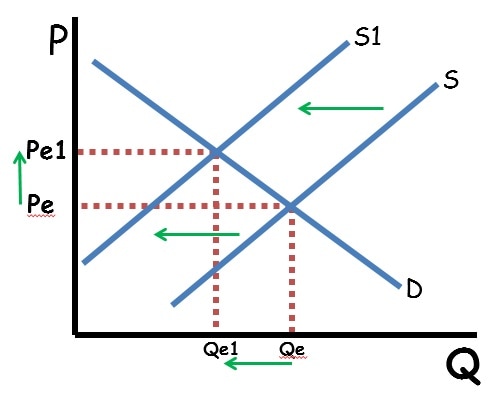
Shifts in supply or demand curves move the equilibrium price and quantity. If demand increases, equilibrium price and quantity both increase. If demand decreases, equilibrium price and quantity both decrease. If supply increases, equilibrium price decreases, and quantity increases. If supply decreases, equilibrium price increases and equilibrium quantity decreases.
Note: If you don’t recall what shifts supply and demand, go review your demand and supply shifters.
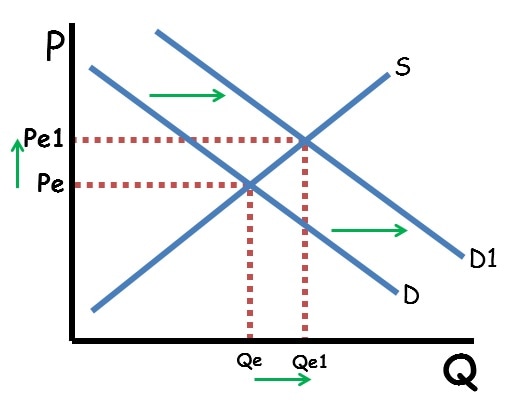
How do double shifts impact price and quantity?
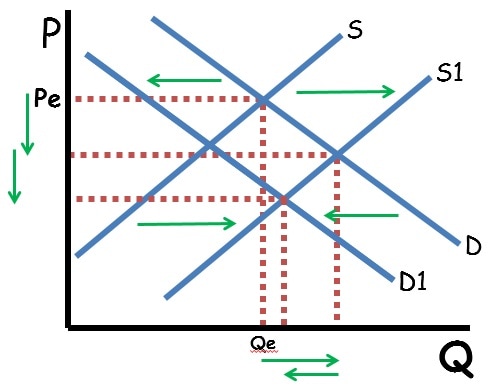
When supply and demand both shift, either price or quantity will be indeterminate. When supply and demand move in the same direction, price is indeterminate. That is because an increase in supply decrease price while an increase in demand will increase price. Since the price axis moves in both directions, the net effect is based on which shift is stronger. Since that cannot be known, the price will be indeterminate. Since both shifts increase equilibrium quantity, the quantity will definitely increase.
Similarly, when supply and demand move in opposite directions, quantity is indeterminate because one shift will increase quantity and the other will decrease quantity.
The key to figuring out the impact of double shifts is to graph out both shifts and see what happens to the equilibrium price and quantity with each shift. If the shifts conflict, that axis is indeterminate.

Multiple Choice Connections:
2012 Released AP Microeconomics Exam Questions: 3, 32, 35
Up Next:
Review Game: Shifting Markets and Prices, Points, and Quantities
Graph Drawing Practice: Perfectly Competitive Market
Content Review Page: Economic Surplus and Deadweight Loss
